Severe Arch Pain In Foot
Overview
We all experience sore arches now and again after a long hike, standing in a long line or walking from one end to the other of a big shopping mall. It's normal for feet to get tired out sometimes, and there's usually no need to worry unless the pain persists. If you're turning to the web because it's dawning on you that your arches are sore several days a week, or maybe even every day, you're doing a smart thing. Chronic pain in the arches can actually be a symptom of a significant underlying condition called Plantar Fasciitis that requires attention and treatment to prevent it from worsening. This article will quickly point out what you need to know about arch pain and Plantar Fasciitis and provide you with resources for learning how to recover.

Causes
At the other end of the spectrum, yet within the same category of congenital flat foot, exist several rare, more severe forms of flat foot. These severe conditions include Vertical Talus, Congenital Calcaneal Valgus, and Tarsal Coalitions - all of which are more rigid (no arch with or without weight on the foot) and definitely symptomatic. Luckily, these are much less common, but can usually be identified by specialists at the time of presentation and treated appropriately. The second category, acquired flat foot, develops over time, rather than at birth. Many different factors can contribute to the development of flat feet. These include the types of shoes a child wears, a child's sitting or sleeping positions, compensation for other abnormalities further up the leg, or more severe factors such as rupture of ligaments or tendons in the foot. Very commonly, the reason for flat feet is that the foot is compensating for a tight Achilles tendon. If the Achilles tendon is tight, then it causes the foot to point down, or to plantarflex (as occurs when stepping on the accelerator of your car). Even minimal amounts of plantarflexion can simulate a longer leg on that particular side, assuming that the other foot is in the normal position. The body therefore tries to compensate by pronating, or flattening out the arch, thereby making up for the perceived extra length on the affected side.
Symptoms
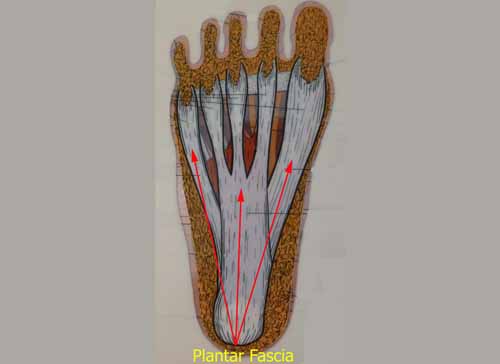
The most common symptoms of plantar fasciitis include pain on the bottom of the foot near the heel, pain with the first few steps after getting out of bed in the morning, or after a long period of rest, such as after a long car ride. The pain subsides after a few minutes of walking. Greater pain after (not during) exercise or activity.
Diagnosis
Flat feet are easy to identify while standing or walking. When someone with flat feet stands, their inner foot or arch flattens and their foot may roll over to the inner side. This is known as overpronation. To see whether your foot overpronates, stand on tiptoes or push your big toe back as far as possible. If the arch of your foot doesn't appear, your foot is likely to overpronate when you walk or run. It can be difficult to tell whether a child has flat feet because their arches may not fully develop until they're 10 years of age.
Non Surgical Treatment
Flat feet in a child do not need treatment if they are not causing pain or walking problems. Your child's feet will grow and develop the same, whether special shoes, shoe inserts, heel cups, or wedges are used. Your child may walk barefoot, run or jump, or do any other activity without making the flat feet worse. In older children and adults, flexible flat feet that do not cause pain or walking problems do not need further treatment. If you have pain due to flexible flat feet, the following may help. An arch-support (orthotic) that you put in your shoe. You can buy this at the store or have it custom-made. Special shoes. Rigid or painful flat feet need to be checked by a health care provider. The treatment depends on the cause of the flat feet. For tarsal coalition, treatment starts with rest and possibly a cast. Surgery may be needed if pain does not improve. In more severe cases, surgery may be needed to clean or repair the tendon, fuse joints in the foot into a corrected position. Flat feet in older adults can be treated with pain relievers, orthotics, and sometimes surgery.
Surgical Treatment
The procedure involves cutting and shifting the bone, and then performing a tendon transfer. First, the surgeon performs a calcaneal osteotomy, cutting the heel bone and shifting it into the correct position. Second, the surgeon transfers the tendon. Reroute the flexor digitorum to replace the troublesome posterior tibial tendon. Finally, the surgeon typically performs one or more fine-tuning procedures that address the patient?s specific foot deformity. Often, the surgeon will lengthen the Achilles tendon because it is common for the mispositioned foot to cause the Achilles to tighten. Occasionally, to increase the arch, the surgeon performs another osteotomy of one of the bones of the midfoot. Occasionally, to point the foot in a straightforward direction, the surgeon performs another osteotomy of the outside portion of the calcaneus.
Stretching Exercises
Plantar Fasciitis stretches can be incorporated into a comprehensive treatment regime which may involve: ice, heel wedge support, taping, massage, muscle strengthening, orthotic inserts for shoes, topical anti inflammatory gel or oral medication and/or corticosteroid injections. If you suspect you may have Plantar Fasciitis seek accurate diagnosis and treatment from a health professional to ensure a correct diagnosis and reduce the likelihood of developing chronic foot pain. Treatment interventions may be provided by your Physical Therapist, Podiatrist and/or doctor.
We all experience sore arches now and again after a long hike, standing in a long line or walking from one end to the other of a big shopping mall. It's normal for feet to get tired out sometimes, and there's usually no need to worry unless the pain persists. If you're turning to the web because it's dawning on you that your arches are sore several days a week, or maybe even every day, you're doing a smart thing. Chronic pain in the arches can actually be a symptom of a significant underlying condition called Plantar Fasciitis that requires attention and treatment to prevent it from worsening. This article will quickly point out what you need to know about arch pain and Plantar Fasciitis and provide you with resources for learning how to recover.

Causes
At the other end of the spectrum, yet within the same category of congenital flat foot, exist several rare, more severe forms of flat foot. These severe conditions include Vertical Talus, Congenital Calcaneal Valgus, and Tarsal Coalitions - all of which are more rigid (no arch with or without weight on the foot) and definitely symptomatic. Luckily, these are much less common, but can usually be identified by specialists at the time of presentation and treated appropriately. The second category, acquired flat foot, develops over time, rather than at birth. Many different factors can contribute to the development of flat feet. These include the types of shoes a child wears, a child's sitting or sleeping positions, compensation for other abnormalities further up the leg, or more severe factors such as rupture of ligaments or tendons in the foot. Very commonly, the reason for flat feet is that the foot is compensating for a tight Achilles tendon. If the Achilles tendon is tight, then it causes the foot to point down, or to plantarflex (as occurs when stepping on the accelerator of your car). Even minimal amounts of plantarflexion can simulate a longer leg on that particular side, assuming that the other foot is in the normal position. The body therefore tries to compensate by pronating, or flattening out the arch, thereby making up for the perceived extra length on the affected side.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of plantar fasciitis include pain on the bottom of the foot near the heel, pain with the first few steps after getting out of bed in the morning, or after a long period of rest, such as after a long car ride. The pain subsides after a few minutes of walking. Greater pain after (not during) exercise or activity.
Diagnosis
Flat feet are easy to identify while standing or walking. When someone with flat feet stands, their inner foot or arch flattens and their foot may roll over to the inner side. This is known as overpronation. To see whether your foot overpronates, stand on tiptoes or push your big toe back as far as possible. If the arch of your foot doesn't appear, your foot is likely to overpronate when you walk or run. It can be difficult to tell whether a child has flat feet because their arches may not fully develop until they're 10 years of age.
Non Surgical Treatment
Flat feet in a child do not need treatment if they are not causing pain or walking problems. Your child's feet will grow and develop the same, whether special shoes, shoe inserts, heel cups, or wedges are used. Your child may walk barefoot, run or jump, or do any other activity without making the flat feet worse. In older children and adults, flexible flat feet that do not cause pain or walking problems do not need further treatment. If you have pain due to flexible flat feet, the following may help. An arch-support (orthotic) that you put in your shoe. You can buy this at the store or have it custom-made. Special shoes. Rigid or painful flat feet need to be checked by a health care provider. The treatment depends on the cause of the flat feet. For tarsal coalition, treatment starts with rest and possibly a cast. Surgery may be needed if pain does not improve. In more severe cases, surgery may be needed to clean or repair the tendon, fuse joints in the foot into a corrected position. Flat feet in older adults can be treated with pain relievers, orthotics, and sometimes surgery.

Surgical Treatment
The procedure involves cutting and shifting the bone, and then performing a tendon transfer. First, the surgeon performs a calcaneal osteotomy, cutting the heel bone and shifting it into the correct position. Second, the surgeon transfers the tendon. Reroute the flexor digitorum to replace the troublesome posterior tibial tendon. Finally, the surgeon typically performs one or more fine-tuning procedures that address the patient?s specific foot deformity. Often, the surgeon will lengthen the Achilles tendon because it is common for the mispositioned foot to cause the Achilles to tighten. Occasionally, to increase the arch, the surgeon performs another osteotomy of one of the bones of the midfoot. Occasionally, to point the foot in a straightforward direction, the surgeon performs another osteotomy of the outside portion of the calcaneus.
Stretching Exercises
Plantar Fasciitis stretches can be incorporated into a comprehensive treatment regime which may involve: ice, heel wedge support, taping, massage, muscle strengthening, orthotic inserts for shoes, topical anti inflammatory gel or oral medication and/or corticosteroid injections. If you suspect you may have Plantar Fasciitis seek accurate diagnosis and treatment from a health professional to ensure a correct diagnosis and reduce the likelihood of developing chronic foot pain. Treatment interventions may be provided by your Physical Therapist, Podiatrist and/or doctor.